


Uses a partially permeable membrane to remove ions, unwanted molecules and larger particles from drinking water. In reverse osmosis, an applied pressure is used to overcome osmotic pressure, a colligative property, that is driven by chemical potential differences of the solvent, a thermodynamic parameter. Reverse osmosis can remove many types of dissolved and suspended chemical species as well as biological ones (principally bacteria) from water, and is used in both industrial processes and the production of potable water.
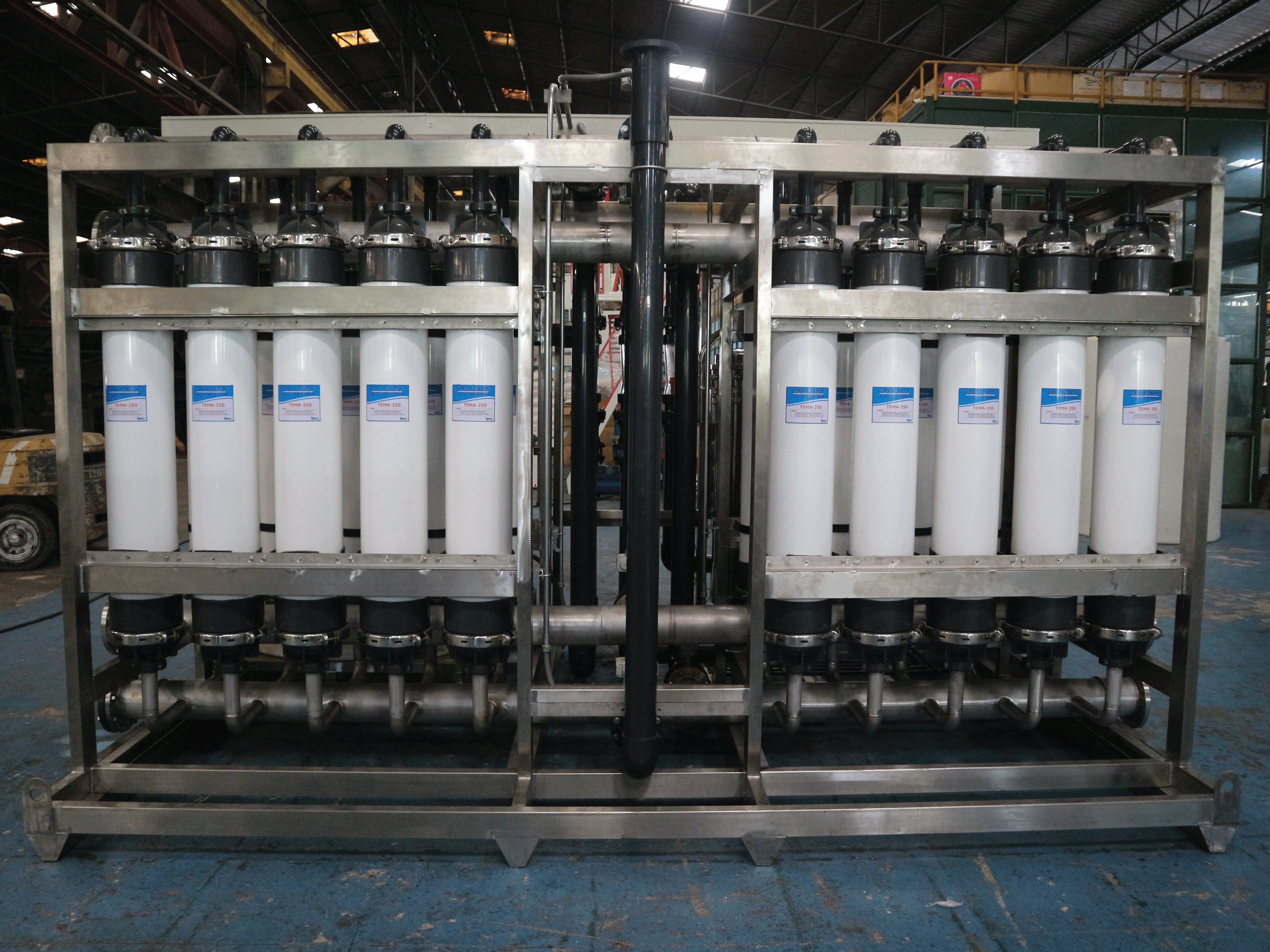
A variety of membrane filtration in which forces like pressure or concentration gradients lead to a separation through a semipermeable membrane. Suspended solids and solutes of high molecular weight are retained in the so-called retentate, while water and low molecular weight solutes pass through the membrane in the permeate (filtrate). This separation process is used in industry and research for purifying and concentrating macromolecular (103 - 106 Da) solutions, especially protein solutions.
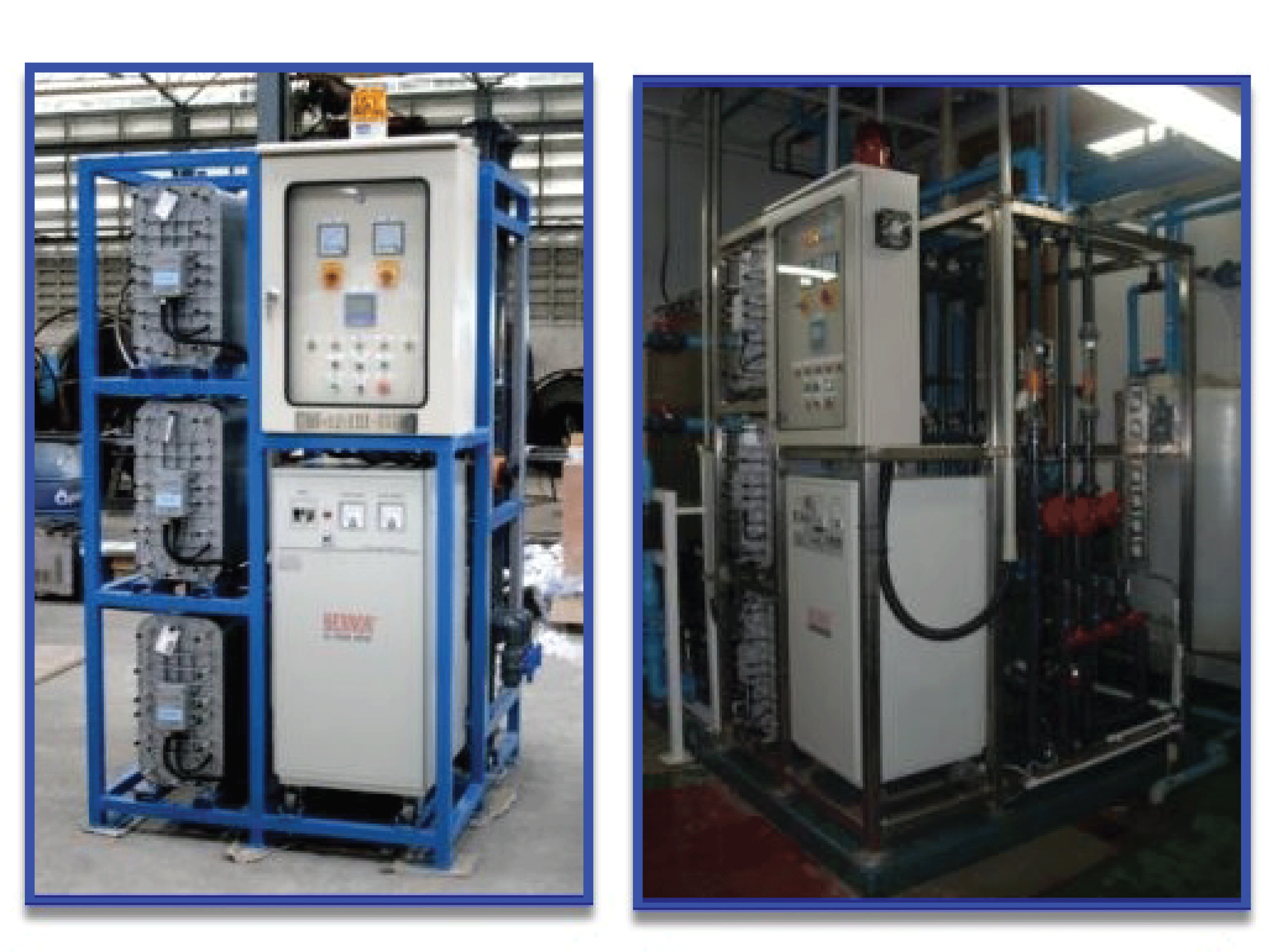
Electrodeionization (EDI) replace the conventional DI mixed resin beds to produce deionized water. Unlike DI resin, EDI does not require shutdowns for replacing resin beds or for resin regeneration using chemicals. EDI removes ions from aqueous streams, typically in conjunction with reverse osmosis (RO) and other purification systems. Our high-quality modules produce pure water and ultrapure water up to 18.2 MΩ.cm. EDI system maybe run continuously or intermittently.